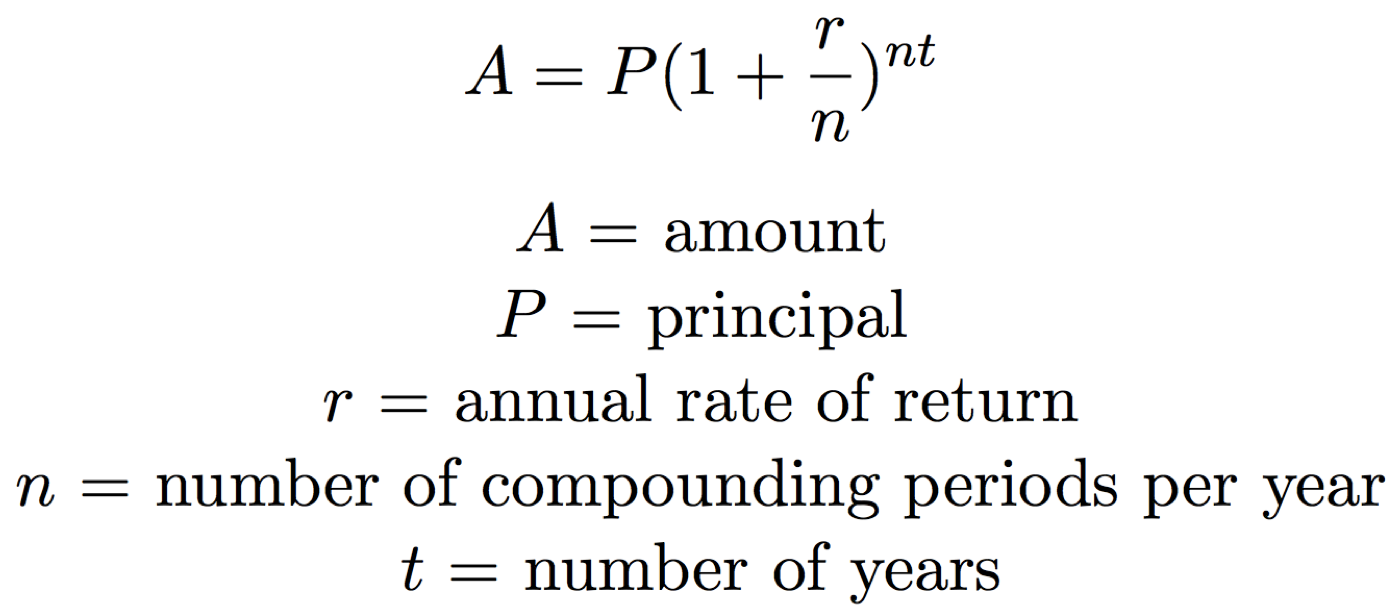
Simple interest refers only to interest earned on the principal balance; interest earned on interest is not taken into account. To see how compound interest differs from simple interest, use our simple interest vs compound average irs and state tax refund and processing times interest calculator. Just enter your beginning balance, the regular deposit amount at any specified interval, the interest rate, compounding interval, and the number of years you expect to allow your investment to grow.
See How Fast Your Money Grows
The effective annual rate (also known as the annual percentage yield) is the rate of interest that you actually receive on your savings or investment aftercompounding has been factored in. So, let’s now break down interest compounding by year,using a more realistic example scenario. We’ll say you have $10,000 in a savings account earning 5% interest per year, withannual compounding. We’ll assume you intend to leave the investment untouched for 20 years. This means that [latex]9\%[/latex] compounded monthly is equal to a periodic interest rate of [latex]0.75\%[/latex] per month.
Use the Bar Chart to Explore Growth Over Time
- Much like a snowball at the top of a hill, compound interest grows your balances a small amount at first.
- Compound interest is often compared to a snowball that grows over time.
- This tool enables you to check how much time you need to double your investment even quicker than the compound interest rate calculator.
For other compounding frequencies (such as monthly, weekly, or daily), prospective depositors should refer to the formula below. There are several formulas for calculating compound interest, depending on the compounding frequency and whether you’ll be making contributions along the way. The assumption here is that this amount is added at the end of the year, so interest won’t be earned in the year that it is added. However, if more than one year is selected, it will earn interest in future years.
Get 5 FREE Video Lessons With Uncommon Insights To Accelerate Your Financial Growth
Enter your initial amount, contributions, rate of return and years of growth to see how your balance increases over time. Tibor has extensively used this calculator in various projects, allowing him to project financial outcomes accurately and advise on investment strategies. It’s become an essential tool for anyone needing to calculate the future value of their investments, considering different compounding frequencies and additional contributions. To compare bank offers that have different compounding periods, we need to calculate the Annual Percentage Yield, also called Effective Annual Rate (EAR). The most comfortable way to figure it out is using the APY calculator, which estimates the EAR from the interest rate and compounding frequency.

Compound Interest Formula (with different periodic payments)
The only thing you must remember is that the interest rate must match your time period. If you are compounding daily, for example, then be sure that you are working with a daily interest rate, or if you are compounding monthly, be sure that you are working with a monthly interest rate. The following chart demonstrates the difference that the number of compounding periods can make for a $10,000 investment with an annual 7% interest rate over a 10-year period. Here’s how different compounding period intervals are affecting the total amount generated and interest earned.
Example 1 – basic calculation of the value of an investment
The process repeats until at the end of three years, you deposit your last $135 that will not accrue interest since you are depositing it on the same day you are checking the balance in your account. Remember also that, because you are compounding quarterly, the annual rate must be divided by four since your deposits are earning interest every quarter. The compounding frequency, which is the time period at which interest is added to the principal, can have a slight positive effect on the effective interest rate versus the nominal annual interest rate.
The Rule of 72 is a simpler way to determine how long it’ll take for a specific amount of money to double, given a fixed return rate of return that is compounded annually. It can be used for any investment, as long as there is a fixed rate that involves compound interest. Simply divide the number 72 by the annual rate of return and the result of this is how many years it’ll take. Our online tools will provide quick answers to your calculation and conversion needs. On this page, you can calculate compound interest with daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, and yearly compounding.
Our flagship wealth planning course teaches you how to secure your financial future with certainty. The depreciation calculator enables you to use three different methods to estimate how fast the value of your asset decreases over time. If you want to head back up to the calculator results area, you can click the link here. If you have any feedback or questionsabout the RoR or TWR, please contact us. It is for this reason that financial experts commonly suggest the risk management strategy of diversification. While things get a bit more complicated when contributions are introduced, these are the steps needed to calculate compound interest.
The more frequently interest is compounded within a time period, the higher the interest will be earned on an original principal. The following is a graph showing just that, a $1,000 investment at various compounding frequencies earning 20% interest. This Compound Interest Calculator can help determine the compound interest accumulation and final balances on both fixed principal amounts and additional periodic contributions. There are also optional factors available for consideration, such as the tax on interest income and inflation. Now, yes, this is a lot of steps, but thankfully we have our formula to calculate that same value in just a few basic algebraic steps. Start by multiply your initial balance by one plus the annual interest rate (expressed as a decimal) divided by the number of compounds per year.
